Blog Post
Sweeteners for Sports Nutrition
Nowadays a lot of different non-nutritive sweeteners are available like sucralose, stevia, acesulfame K, and aspartame. As a manufacturer of sports nutrition it is important to be well-informed on which sweetener to use.
Non-nutritive sweeteners
Non-Nutritive Sweeteners
Non-nutritive sweeteners, also known as artificial sweeteners, are a category of sweetening agents that provide sweetness to foods and beverages without contributing significant calories or providing essential nutrients.Non-nutritive sweeteners are typically many times sweeter than sugar, so only a small amount is needed to achieve the desired level of sweetness.
Sucralose
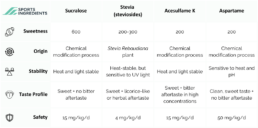
Sucralose is a high-intensity, non-nutritive artificial sweetener that is commonly used as a sugar substitute in a wide range of food and beverage products.

Sweetness: Sucralose is incredibly sweet, approximately 600 times sweeter than sucrose (table sugar). Because it is so much sweeter, only a very small amount is needed to achieve the desired level of sweetness.
Origin: Sucralose is derived from sucrose through a chemical modification process.
Stability: Sucralose is notable for its heat and light stability, which makes it suitable for cooking and baking, as it does not break down when exposed to heat.
Taste Profile: Sucralose is known for its sugar-like taste without the bitter aftertaste associated with some other non-nutritive sweeteners.

Safety: Sucralose has been extensively studied for its safety, and numerous regulatory agencies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have approved its use as a sweetener. It has an established acceptable daily intake (ADI) of 15 mg/kg/d.
Stevia
Stevia is a natural, non-nutritive sweetener derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, which is native to South America.

Sweetness: Stevia is known for its intense sweetness. In its pure form, steviol glycosides, the compounds responsible for the sweet taste, can be up to 200 to 300 times sweeter than sucrose.

Origin: Unlike many artificial sweeteners, stevia is derived from a plant source. The sweet taste in stevia leaves comes from compounds such as stevioside and rebaudioside.

Stability: Stevia, while heat-stable, is sensitive to UV light and should be stored in a dark, cool place to maintain its stability.

Taste Profile: Stevia has a sweet taste, but it can have a mild, licorice-like or herbal aftertaste.

Safety: Stevia has been reviewed for safety by various regulatory agencies, including the U.S. FDA. It is generally considered safe for most people when consumed within established ADI levels of 4 mg/kg/d.
Acesulfame K
Acesulfame K, also known as acesulfame potassium or Ace-K, is a non-nutritive artificial sweetener commonly used as a sugar substitute in various food and beverage products.

Sweetness: Acesulfame K is a high-intensity sweetener, approximately 200 times sweeter than sucrose.

Origin: Acesulfame K is created through a chemical modification process.

Stability: Acesulfame K is notable for its heat and light stability. This stability makes it suitable for use in cooking and baking.

Taste Profile: Acesulfame K is known for its clean, neutral taste but can have a bitter aftertaste in high concentrations.

Safety: Acesulfame K has undergone extensive safety assessments and has been approved for use by regulatory agencies, including the U.S. FDA. It has an established ADI of 15 mg/kg/d.
Aspartame
Aspartame is a low-calorie artificial sweetener that is widely used as a sugar substitute in various food and beverage products.

Sweetness: Aspartame is approximately 200 times sweeter than sucrose (table sugar).

Origin: Aspartame is created through a chemical process by combining two amino aids.

Stability: Aspartame is sensitive to heat and breaks down when exposed to high temperatures, which can limit its use in cooking and baking. It is also sensitive to changes in pH, and its sweetness can diminish in acidic conditions.

Taste Profile: Aspartame provides a clean, sweet taste without the bitter aftertaste that some other artificial sweeteners may have.

Safety: Aspartame has undergone extensive safety testing and has been approved for consumption by numerous regulatory agencies around the world, including the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The ADI for aspartame is set at 50 mg/kg/d.

PKU: Aspartame is not recommended for individuals with a rare genetic disorder called phenylketonuria (PKU) because they cannot metabolize phenylalanine, one of aspartame's components, and it can accumulate to toxic levels in their bodies.
Other influences
Other Influences on the Perception of Sweetness
Color
Influences of Color
The color of a product can create expectations about its taste. When consumers see a vibrant, sweet color like red or orange, they may anticipate a certain level of sweetness. If the product's actual sweetness level doesn't match this visual expectation, it can lead to a disconnect between what the taste buds experience and what the eyes perceive.
Certain colors are associated with specific flavors or sweetness levels. Red is often associated with sweetness:
A red colorant may lead consumers to perceive it as sweeter than it actually is A product with a color that doesn't align with typical sweetness expectations may be perceived as less sweet.
Odor
Influences of Odor
The brain combines taste and aroma to create the overall perception of flavor. When you consume a product, the volatile compounds that make up its aroma interact with your olfactory receptors.
Certain odors can enhance the perception of sweetness. Fruity or floral aromas are often associated with sweetness.
When you smell these types of aromas while consuming a product, they can enhance your perception of sweetness, making the product taste sweeter than it actually is.
We advise on the use of Sweeteners in Sports Nutrition
Non-nutritive sweeteners like sucralose, stevia, acesulfame K, and aspartame are popular sugar substitutes that provide sweetness without significant calories. These sweeteners have different levels of sweetness and stability. It's important as a manufacturer to know the characteristics of the sweeteners and how to use them.
REFERENCES
References
Food & Drug Administration [FDA]. (2023). Aspartame and Other Sweeteners in Food. U.S. Food And Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/food/food-additives-petitions/aspartame-and-other-sweeteners-food
Related Products
How to read extract ratios?
Misunderstandings on what plant-to-extract ratios signify are common. These ratios are often thought to indicate the amount of active ingredient present or the purity of the extract. These are both common misinterpretations of plant-to-extract ratio’s. This blog post will tell you more about what these plant-to-extract ratios actually mean.
Protein content determination: is it always accurate?
Products containing protein are required to list the protein content on their nutritional labels. The determination and calculation of this protein content are commonly performed using the Kjeldahl method. This method measures the amount of nitrogen in the product to estimate its protein content. This blog will explain the Kjeldahl method and assess its accuracy.
Gastro-resistance explained
Nowadays dietary supplements are occasionally labelled gastro-resistant. Often the question arises what does gastro-resistant mean and what is it good for? This blog will give more insight into gastro-resistant supplements and their benefits.
Private Label Clear Vegan Protein
We are happy to unveil our latest product innovation – Clear Vegan Protein, designed to meet the evolving demands of the health and wellness market. This formula offers a refreshing and customizable alternative to traditional plant-based proteins, making it an ideal addition to your product lineup. Need help to kickstart your next Private Label Clear Vegan Protein? Let us help you to produce it.
Labelling Requirements for Sports Nutrition
In the fast-paced world of sports nutrition, where performance and precision are paramount, it is critical to understand the importance of regulatory compliance and transparency. Whether you're a manufacturer, distributor, or retailer of sports nutrition products, adhering to precise labelling requirements is not only a legal obligation but also a key component of maintaining the trust and loyalty of your customers.
Heat Stability of Proteins in Sports Nutrition
Proteins, the building blocks of life, undergo a fascinating transformation when exposed to heat. As a manufacturer, understanding the heat stability of proteins adds a layer of knowledge that can be important in Sports Nutrition.
The Role of Sugar Intake During Exercise
In the pursuit of peak athletic performance, the importance of nutrition cannot be overstated. Among the various nutrients that fuel our bodies, carbohydrates play a pivotal role, especially during exercise. As athletes strive to optimize their performance, understanding the impact of sugar intake during exercise is crucial. In this blog post, we delve into the science behind sugar consumption during physical activity.